Association of British Clinical Diabetologists (ABCD) and Diabetes UK joint position statement and recommendations for non-diabetes specialists on the use of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in people with type 2 diabetes (January 2021)

ABSTRACT
Sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are now an established class of medications for the treatment of type 2 diabetes (T2D), no longer reserved for use by specialists in diabetes. They are being used increasingly for their cardiac and renal benefits by primary care, cardiology and renal teams for indications in parallel with diabetes care as part of holistic management. This guidance provides essential information on SGLT therapy, including the main advantages and the important risks of which healthcare professionals should be aware.
What is new?
The American Diabetes Association / European Association for the Study of Diabetes (ADA/EASD) consensus report 2019 update recommends the use of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors with proven cardiovascular and renal benefits as a second-line therapy independent of glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) target after metformin when there is a need to address atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (previous myocardial infarction, angina or peripheral vascular disease), heart failure, renal impairment, excess body weight or risk of hypoglycaemia.1
SGLT2 inhibitors are being increasingly used in primary care and by non-diabetes specialist teams.
SGLT2 inhibitors are commonly associated with genital mycotic infections. They are also associated with a small increase in risk of diabetic ketoacidosis in people with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Here, we summarise available evidence and provides guidance on how to reduce adverse effects of SGLT2 therapy and manage them when they occur.
What are the types of diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is caused by the destruction of the insulin producing beta cells in the pancreas.2 People with this type of diabetes rapidly become dependent on insulin for survival. Insulin supplementation should never be stopped even for a short period in absolute insulin deficiency as this risks diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
T2D develops because of a mix of resistance to insulin action and deficiency of insulin secretion with variable genetic susceptibility combined with environmental factors (like sedentary lifestyle or obesity). Pharmacotherapy is often required if diet and exercise alone are not sufficient to control diabetes. Metformin is the first-line therapy. SGLT2 inhibitors or glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) analogues with proven cardiovascular benefit are increasingly being used as a second-line therapy based on recent clinical trial results. As diabetes progresses, combination therapy may be needed and insulin may be required to manage hyperglycaemia. Some people with apparent T2D may actually have a slowly progressing T1D (latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA) with positive insulin auto-antibodies) or damage to their entire pancreas (type 3c diabetes). These people are at higher risk of DKA. Other groups with T2D are also ketosis-prone for unknown reasons.3 T2D may present with DKA in some people (particularly of Black ethnicity) but these people often do not require insulin in the long term. In addition, people with T2D and severe illness can have an increase in insulin requirement that precipitates DKA.
How is diabetes diagnosed?
Diabetes is diagnosed by a single fasting plasma glucose ≥7 mmol/L or an HbA1c ≥48 mmol/L in the presence of osmotic symptoms (polydipsia, polyuria, tiredness or thirst) or the same levels on two different occasions in the absence of symptoms.2 Up to 90% of people with T1D have positive auto-antibodies at presentation. Serum or urine C-peptide is initially low, but present. This declines with time, such that C-peptide becomes undetectable in most by 5 years. C-peptide production also decreases in T2D, although much more slowly.
The unmet need in the treatment of people with T2D
Up to 50% of people with T2D die from cardiovascular disease with the increased mortality strongly attributed to diabetic kidney disease.4,5 Therefore, drugs with robust evidence of reducing cardiovascular and renal morbidity and mortality in people with T2D need to be used widely. Additionally, a number of treatment options for T2D are associated with unwanted side effects (such as hypoglycaemia and weight gain). Efficacious drugs not associated with such side effects are also highly desirable.6
What are SGLT2 inhibitors?
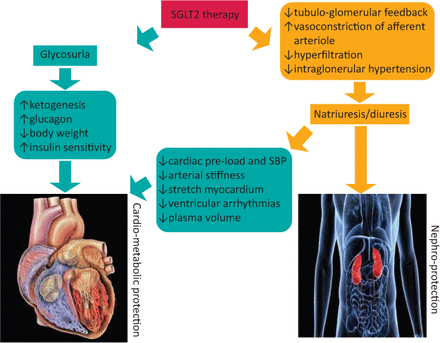
SGLT2 inhibitors are an established class of medications for the treatment of diabetes which act by preventing the absorption of glucose and sodium, mainly from the proximal renal tubule in the kidney. Glucose and sodium are, therefore, lost in urine. People do not become hyponatraemic (unless on diuretics as well) as most of the sodium is reabsorbed in the distal tubule. This effect results in decreasing the blood glucose level, weight loss, an osmotic diuresis and a drop in blood pressure (Fig 1).7 These drugs have been licensed and used widely in people with T2D and have shown significant cardiovascular and kidney benefits in different subsets of this group of patients.8
Cardiovascular and renal effects of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors.7 SBP = systolic blood pressure; SGLT2 = sodium glucose co-transporter 2.
What are the benefits of using SGLT2 inhibitors?
Clinical trials using SGLT2 inhibitors have provided strong evidence in the trial population for reduced risk of major cardiovascular, renal and heart failure events (Tables 1 and 2: evidence differs for different agents within the class) in addition to reducing HbA1c by up to 10 mmol/mol (1.0%) depending upon the initial HbA1c. These medications are associated with a low incidence of hypoglycaemia, weight loss of up to 3 kg of body weight and a reduction in systolic blood pressure of approximately 3–5 mmHg. It is important to select the right patient for SGLT2 inhibitors in order to achieve health benefits (Box 1) without precipitating complications like DKA (Table 3).
Major sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor trials: summary of outcomes
Summary of licensed indications and recommended doses of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in type diabetes
Who is likely to be at risk with sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors?
What to do when initiating SGLT2 inhibitors: information for the patient
Treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors should be initiated only after ensuring adequate understanding of the person in the following aspects.
Discuss individualised benefits of taking SGLT2 Inhibitors.
Common side effects (Table 4).
Uncommon side effects (Table 4).
Foot care (Table 4).
Drink plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration unless you have been told to restrict fluids by your healthcare professionals due to heart or kidney problems or some other reason.
How to reduce the risk? Educate the patient about sick day guidance and DKA
When a person with diabetes is not well and is unable to eat and drink as normal, some simple rules can prevent further deterioration or DKA.18
If ill with diarrhoea, vomiting or fever and unusual drowsiness, stop SGLT2 inhibitors and don't restart until feeling better and eating/drinking fluids normally.
When people with diabetes who take insulin are not able to eat, it may be possible for them to consume half a glass of milk or fruit juice or yogurt or soup (not clear soup) in place of meals and follow individualised advice from their healthcare professionals about what dose of insulin to take.
Drink plenty of water / sugar-free fluid to avoid dehydration for up to 24 hours.
Seek medical advice if particularly unwell with infection or illness.
DKA is an uncommon but serious side effect characterised by the build-up of acidic chemicals in the blood called ketones.23
Ketones are produced due to insulin deficiency in the body which can be absolute or relative.
Illness, infections, starvation, carbohydrate deficient diet, excessive exercise, alcohol, surgery, illicit drugs, reduced insulin dose (if on insulin) and dehydration increase the risk of DKA.
Be aware that glucose levels can be normal because of the way SGLT2 inhibitors work. Thus, ketone levels can be high even with a normal glucose!
If you have nausea, vomiting, abdomen pain, stupor, fatigue and difficulty breathing, then you or people close to you should suspect DKA and seek immediate medical advice.
Urine ketone levels are not always reliable. Test your capillary ketone if you have a ketone meter or go to your local hospital for blood ketone testing.
If ketones are >1.5 mmol/L, further blood tests may be needed to confirm or exclude DKA.
As ketones may lead to worse surgical outcome, SGLT inhibitors should be stopped 48 hours before elective surgery. However, ketones should be tested for in the presence of symptoms suggestive of DKA even after interruption of SGLT2 inhibitors. In addition, ketones should be periodically checked (as required) if the admission is for emergency surgery. SGLT2 inhibitors can be restarted 24 hours after resuming normal oral intake.
Useful information has been produced by national cardiology, renal and metabolic associations which can be downloaded and shared with people with diabetes.24
What to do when initiating SGLT2 inhibitors: information for the prescriber
When SGLT2 inhibitors are started, the healthcare provider should document completion of the education session with the person with diabetes and offer some advice on who to contact if the person taking the SGLT2 inhibitor is not feeling well. Glucose lowering medications that may cause hypoglycaemia, such as insulin and sulphonylureas, should be reviewed and consideration should be given to reduce the dose when SGLT2 inhibitor is started, particularly if the individual's HbA1c is at target when the treatment is being initiated. If the insulin requirement reduces considerably, one should be cautious of a higher risk of developing DKA. The healthcare professional should review diuretic and anti-hypertensive therapy periodically if hypertension improves or if there is postural hypotension.
How to reduce the risk of DKA and manage it? Educate the health professionals
In patients with diabetes on SGLT2 inhibitors with symptoms suggestive of DKA, ketosis should be confirmed by measuring capillary or venous blood ketone. If the ketone levels are above 1.5 mmol/L, acidosis should be checked by measuring venous bicarbonate (<18 mmol/L) or venous pH (<7.38). Blood glucose level in this situation can be normal because SGLT2 inhibitors induce glucose excretion. If DKA is confirmed (ketones >3.0 mmol/L, bicarbonate <15 mmol/L and pH <7.30), then the severity will be assessed by local criteria and treated according to the Joint British Diabetes Society (JBDS) guidelines or a locally adapted protocol.23 Intravenous glucose in addition to fixed rate insulin infusion may be required to avoid hypoglycaemia while treating euglycaemic DKA.
When to stop treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors?
It is useful to remember that SGLT2 inhibitors may have to be temporarily stopped in situations which can increase the risk of DKA. Healthcare professionals should be especially careful in the following situations. After an episode of DKA the medications should not be restarted in future.
Suspend SGLT2 inhibitors in the following circumstances:
acute medical admission including COVID-19
admission for elective surgery or procedure requiring starvation
vomiting
dehydration.
Restart only AFTER patient has been eating normally for AT LEAST 24 hours AND no longer acutely unwell.
Alternative diabetes treatment may be required in the interim.
In summary, SGLT2 inhibitors are a major advance in the management of T2D with additional cardiovascular and renal benefits. These drugs are now being commonly used by primary care physicians, cardiologists and nephrologists and some understanding of their potential benefits and possible side effects is critical.
Acknowledgement
A version of this paper, adapted for a primary care audience, is due to be published in Dashora U, Wheatcroft S, Winocour P et al; on behalf of the CaReMe UK partnership. Take a holistic approach to the management of diabetes and co-morbidities. Guidelines in Practice 2021;24. www.guidelinesinpractice.co.uk/456004.article
- © Royal College of Physicians 2021. All rights reserved.
References
- ↵
- Buse JB
- ↵
- American Diabetes Association
- ↵
- Dhatariya KK
- ↵
- World Health Organization
- ↵
- Afkarian M
- ↵
- ↵
- De Block C.
- ↵
- Loutradis C
- ↵
- Electronic Medicines Compendium
- ↵
- Electronic Medicines Compendium
- ↵
- Electronic Medicines Compendium
- ↵
- Dashora U
- ↵
- Electronic Medicines Compendium
- Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency
- ↵
- European Medicines Agency
- Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency
- ↵
- ↵
- British Cardiovascular Society
Article Tools
Citation Manager Formats
Jump to section
- Article
- ABSTRACT
- What is new?
- What are the types of diabetes?
- How is diabetes diagnosed?
- The unmet need in the treatment of people with T2D
- What are SGLT2 inhibitors?
- What are the benefits of using SGLT2 inhibitors?
- What to do when initiating SGLT2 inhibitors: information for the patient
- How to reduce the risk? Educate the patient about sick day guidance and DKA
- What to do when initiating SGLT2 inhibitors: information for the prescriber
- How to reduce the risk of DKA and manage it? Educate the health professionals
- When to stop treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors?
- Acknowledgement
- References
- Figures & Data
- Info & Metrics
Related Articles
- No related articles found.