Abstract
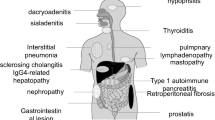
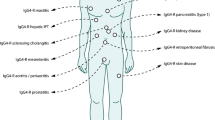
Recent studies have suggested the existence of two subtypes of autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP): type 1 AIP, related to IgG4 (lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis); and type 2 AIP, related to a granulocytic epithelial lesion (idiopathic duct-centric chronic pancreatitis). Compared with type 2 AIP, the clinicopathological features of type 1 AIP, with increased serum IgG4/IgE levels, abundant infiltration of IgG4 + plasmacytes and lymphocytes, autoantibodies, and steroid responsiveness, are more suggestive of abnormal immunity such as allergy or autoimmunity. Moreover, patients with type 1 AIP often have extrapancreatic lesions, such as sclerosing cholangitis, sclerosing sialadenitis, or retroperitoneal fibrosis, showing pathological features similar to those of the pancreatic lesions. Based on these findings, an international concept of and diagnostic criteria for AIP have been proposed recently. Of interest, many synonyms have been proposed for the conditions of AIP and extrapancreatic lesions associated with IgG4, such as “multifocal idiopathic fibrosclerosis,” “IgG4-related autoimmune disease,” “IgG4-related sclerosing disease,” “systemic IgG4-related plasmacytic syndrome (SIPS),” and “IgG4-related multiorgan lymphoproliferative syndrome,” all of which may refer to the same conditions. Therefore, the Japanese Research Committee for “Systemic IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease” proposed a disease concept and clinical diagnostic criteria based on the concept of multifocal fibrosclerosing disease, in 2009, in which the term “IgG4-related disease” was agreed upon as a minimal consensus to cover these conditions. Although the significance of IgG4 in the development of “IgG4-related disease” remains unclear, we have proposed a hypothesis for the development of type 1 AIP, one of the IgG4-related diseases. The concept and diagnostic criteria of “IgG4-related disease” will be changed in accordance with future studies.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AIP:
-
Autoimmune pancreatitis
- ANA:
-
Anti-nuclear antibody
- CA-II:
-
Carbonic anhydrase-II
- CTLA-4:
-
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4
- ERCP:
-
Endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography
- FCRL:
-
Fc-receptor-like
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon-γ
- IL-4:
-
Interleukin-4
- LF:
-
Lactoferrin
- LPSP:
-
Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis
- MD:
-
Mikulicz disease
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- MOLPS:
-
Multiorgan lymphoproliferative disease
- PBP:
-
Plasminogen-binding protein
- SjS:
-
Sjögren’s syndrome
- PSC:
-
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- RF:
-
Rheumatoid factor
- SIPS:
-
Systemic IgG4 plasmacytic syndrome
- SLE:
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Treg:
-
Regulatory T cell
- UBR2:
-
Ubiquitin-protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 2
References
Sarles H, Sarles JC, Muratore R, Guien C. Chronic inflammatory sclerosis of the pancreas—an autonomous pancreatic disease? Am J Dig Dis. 1961;6:688–98.
Yoshida K, Toki F, Takeuchi T, Watanabe S, Shiratori K, Hayashi N. Chronic pancreatitis caused by an autoimmune abnormality. Proposal of the concept of autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1995;40:1561–8.
Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. New Engl J Med. 2001;344:732–8.
Okazaki K, Uchida K, Chiba T. Recent concept of autoimmune-related pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2001;36:293–302.
Okazaki K, Kawa S, Kamisawa T, Naruse S, Tanaka S, Nishimori I, et al. Clinical diagnostic criteria of autoimmune pancreatitis: revised proposal. J Gastroenterol. 2006;41:626–31.
Pickartz T, Mayerle J, Lerch M. Autoimmune pancreatitis. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;4:314–23.
Kawaguchi K, Koike M, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A, Tabata I, Fujita N. Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis with cholangitis: a variant of primary sclerosing cholangitis extensively involving pancreas. Hum Pathol. 1991;22:387–95.
Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:982–4.
Comings DE, Skubi KB, Van Eyes J, Motulsky AG. Familial multifocal fibrosclerosis. Ann Intern Med. 1967;66:884–92.
Chari ST, Kloeppel G, Zhang L, Notohara K, Lerch MM, Shimosegawa T, et al. Histopathologic and clinical subtypes of autoimmune pancreatitis: the Honolulu consensus document. Pancreas. 2010;39:549–54.
Klöppel G, Detlefsen S, Chari ST, Longnecker DS, Zamboni G. Autoimmune pancreatitis: the clinicopathological characteristics of the subtype with granulocytic epithelial lesions. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:787–93.
Notohara K, Burgart LJ, Yadav D, Chari S, Smyrk TC. Idiopathic chronic pancreatitis with periductal lymphoplasmacytic infiltration: clinicopathologic features of 35 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27:1119–27.
Zamboni G, Luttges J, Capelli P, Frulloni L, Cavallini G, Pederzoli P, et al. Histopathological features of diagnostic and clinical relevance in autoimmune pancreatitis: a study on 53 resection specimens and 9 biopsy specimens. Virchows Arch. 2004;445:552–63.
Mikulicz J. Über eine eigenartige symmetrishe Erkrankung der Tränen und Mundspeicheldrüsen. Stuttgart: Beitr z Chir Festschr f Theodor Billroth; 1892. p. 610–30.
Saeki T, Nishi S, Imai N, Ito T, Yamazaki H, Kawano M, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of patients with IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2010;78:1016–23.
Li Y, Nishihara E, Hirokawa M, Taniguchi E, Miyauchi A, Kakudo K. Distinct clinical, serological, and sonographic characteristics of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis based with and without IgG4-positive plasma cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:1309–17.
Kamisawa T, Okamoto A. Autoimmune pancreatitis: proposal of IgG4-related sclerosing disease. J Gastroenterol. 2006;41:613–25.
Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Ohara M, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Yamamoto H, Shinomura Y, Imai K. A new conceptualization for Mikulicz’s disease as an IgG4-related plasmacytic disease. Mod Rheumatol. 2006;16:335–40.
Masaki Y, Dong L, Kurose N, Kitagawa K, Morikawa Y, Yamamoto M, et al. Proposal for a new clinical entity, IgG4-positive multi-organ lymphoproliferative syndrome: analysis of 64 cases of IgG4-related disorders. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:1310–5.
Mackay IR. Autoimmune disease. Med J Aust. 1969;1:696–9.
Detlefsen S, Bräsen JH, Zamboni G, Capelli P, Klöppel G. The position of complement C3c, immunoglobulin (Ig)G4 and IgG at the basement membrane of pancreatic ducts and acini in autoimmune pancreatitis. Histopathology. 2010;57:825–35.
Shimosegawa T, Chari ST, Frulloni L, Kamisawa T, Kawa S, Mino-Kenudson M, et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: guidelines of the International Association Of Pancreatology. Pancreas (in press).
Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A, Amemiya K, et al. Close relationship between autoimmune pancreatitis and multifocal fibrosclerosis. Gut. 2003;52:683–7.
Saegusa H, Momose M, Kawa S, Hamano H, Ochi Y, Takayama M, et al. Hilar and pancreatic gallium-67 accumulation is characteristic feature of autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2003;27:20–5.
Erkelens GW, Vleggaar FP, Lesterhuis W, van Buuren HR, van der Werf SD. Sclerosing pancreato-cholangitis responsive to steroid therapy. Lancet. 1999;354:43–4.
Nakazawa T, Ohara H, Yamada T, Ando H, Sano H, Kajino S, et al. Atypical primary sclerosing cholangitis cases associated with unusual pancreatitis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2001;48:625–30.
Hamano H, Kawa S, Ochi Y, Unno H, Shiba N, Wajiki M, et al. Hydronephrosis associated with retroperitoneal fibrosis and sclerosing pancreatitis. Lancet. 2002;359:1403–4.
Takeda S, Haratake J, Kasai T, Takaeda C, Takazakura E. IgG4-associated idiopathic tubulointerstitial nephritis complicating autoimmune pancreatitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19:474–6.
Uchiyama-Tanaka Y, Mori Y, Kimura T, Watanabe S, Nozaki Y, Fujita K, et al. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with autoimmune-related pancreatitis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43:e18–25.
Shimatsu A, Oki Y, Fujisawa I, Sano T. Pituitary and stalk lesions (infundibulo-hypophysitis) associated with immunoglobulin G4-related systemic disease: an emerging clinical entity. Endocr J. 2009;56:1033–41.
Komatsu K, Hamano H, Ochi Y, Takayama M, Muraki T, Yoshizawa K, et al. High prevalence of hypothyroidism in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2005;50:1052–7.
Yoshimura Y, Takeda S, Ieki Y, Takazakura E, Koizumi H, Takagawa K. IgG4-associated prostatitis complicating autoimmune pancreatitis. Intern Med. 2006;45:897–901.
Okazaki K, Uchida K, Matsushita M, Takaoka M. How to diagnose autoimmune pancreatitis by the revised Japanese clinical criteria. J Gastroenterol. 2007;42(Suppl 18):32–8.
Ohara H, Nakazawa T, Sano H, Ando T, Okamoto T, Takada H, et al. Systemic extrapancreatic lesions associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2005;31:232–7.
Hamano H, Arakura N, Muraki T, Ozaki Y, Kiyosawa K, Kawa S. Prevalence and distribution of extrapancreatic lesions complicating autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2006;41:1197–205.
Okazaki K, Kawa S, Kamisawa T, Ito T, Inui K, Irie H, et al. Japanese clinical guidelines for autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2009;38:849–66.
Okazaki K, Kawa S, Kamisawa T, Shimosegawa T, Tanaka M, et al. Japanese consensus guidelines for management of autoimmune pancreatitis: I. Concept and diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:249–65.
Kawa S, Okazaki K, Kamisawa T, Shimosegawa T, Tanaka M, et al. Japanese consensus guidelines for management of autoimmune pancreatitis: II. Extrapancreatic lesions, differential diagnosis. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:355–69.
Kamisawa T, Okazaki K, Kawa S, et al. Japanese consensus guidelines for management of autoimmune pancreatitis: III. Treatment and prognosis of AIP. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:471–7.
Okazaki K, Uchida K, Research Committee Members. Proposal of the concept and diagnostic criteria of IgG4-related disease. Annual reports of Research Committee Of Intractable Diseases supported by Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan. 2009. p. 25–30 (in Japanese).
Masaki Y, Sugai S, Umehara H. IgG4-related diseases including Mikulicz’s disease and sclerosing pancreatitis: diagnostic insights. J Rheumatol. 2010;37:1380–5.
Roitt I. Antibodies. In: Roitt I, editor. Roitt’s essential immunology. 9th ed. London: Blackwell Science; 1997. p. 43–62.
Taguchi M, Kihara Y, Nagashio Y, Yamamoto M, Otsuki M, Harada M. Decreased production of immunoglobulin M and A in autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2009;44:1133–9.
Robinson DS, Larche M, Durham SR. Tregs and allergic disease. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:1389–97.
van der Neut Kolfschoten M, Schuurman J, Losen M, Bleeker WK, Martínez-Martínez P, Vermeulen E, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of human IgG4 antibodies by dynamic Fab arm exchange. Science. 2007;317:1554–7.
Kawa S, Kitahara K, Hamano H, Ozaki Y, Arakura N, Yoshizawa K, et al. A novel immunoglobulin-immunoglobulin interaction in autoimmunity. PLoS One. 2008;3:e1637.
Stanley JR, Amagai M. Pemphigus, bullous impetigo, and the staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1800–10.
Fujii H, Nakatani K, Arita N, Ito MR, Terada M, Miyazaki T, et al. Internalization of antibodies by endothelial cells via fibronectin implicating a novel mechanism in lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2003;64:1662–70.
Aalberse RC, Stapel SO, Schuurman J, Rispens T. Immunoglobulin G4: an odd antibody. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009;39:469–77.
Ruiter B, Knol EF, van Neerven RJ, Garssen J, Bruijnzeel-Koomen CA, Knulst AC, et al. Maintenance of tolerance to cow’s milk in atopic individuals is characterized by high levels of specific immunoglobulin G4. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007;37:1103–10.
Hussain R, Poindexter RW, Ottesen EA. Control of allergic reactivity in human filariasis. Predominant localization of blocking antibody to the IgG4 subclass. J Immunol. 1992;148:2731–7.
Yazdanbakhsh M, van den Biggelaar A, Maizels RM. Th2 responses without atopy: immunoregulation in chronic helminth infections and reduced allergic disease. Trends Immunol. 2001;22:372–7.
Miyoshi H, Uchida K, Taniguchi T, Yazumi S, Matsushita M, Takaoka M, et al. Circulating naive and CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2008;36:133–40.
Zen Y, Fujii T, Harada K, Kawano M, Yamada K, Takahira M, et al. Th2 and regulatory immune reactions are increased in immunoglobin G4-related sclerosing pancreatitis and cholangitis. Hepatology. 2007;45:1538–46.
Cornell LD, Chicano SL, Deshpande V, Collins AB, Selig MK, Lauwers GY, et al. Pseudotumors due to IgG4 immune-complex tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with autoimmune pancreatocentric disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:1586–97.
Muraki T, Hamano H, Ochi Y, Komatsu K, Komiyama Y, Arakura N, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis and complement activation system. Pancreas. 2006;32:16–21.
Uchida K, Okazaki K, Konishi Y, Ohana M, Takakuwa H, Hajiro K, et al. Clinical analysis of autoimmune-related pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:2788–94.
Okazaki K, Uchida K, Ohana M, Nakase H, Uose S, Inai M, et al. Autoimmune-related pancreatitis is associated with autoantibodies and a Th1/Th2-type cellular immune response. Gastroenterology. 2000;118:573–81.
Nishi H, Tojo A, Onozato ML, Jimbo R, Nangaku M, Uozaki H, et al. Anti-carbonic anhydrase II antibody in autoimmune pancreatitis and tubulointerstitial nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007;22:1273–5.
Aparisi L, Farre A, Gomez-Cambronero L, Martinez J, De Las Heras G, Corts J, et al. Antibodies to carbonic anhydrase and IgG4 levels in idiopathic chronic pancreatitis: relevance for diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2005;54:703–9.
Nishimori I, Miyaji E, Morimoto K, Nagao K, Kamada M, Onishi S. Serum antibodies to carbonic anhydrase IV in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2005;54:274–81.
Asada M, Nishio A, Uchida K, Kido M, Ueno S, Uza N, et al. Identification of a novel autoantibody against pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2006;33:20–6.
Endo T, Takizawa S, Tanaka S, Takahashi M, Fujii H, Kamisawa T, et al. Amylase alpha-2A autoantibodies: novel marker of autoimmune pancreatitis and fulminant type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2009;58:732–7.
Takizawa S, Endo T, Wanjia X, Tanaka S, Takahashi M, Kobayashi T. HSP 10 is a new autoantigen in both autoimmune pancreatitis and fulminant type 1 diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;386:192–6.
Frulloni L, Lunardi C, Simone R, Dolcino M, Scattolini C, Falconi M, et al. Identification of a novel antibody associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:2135–42.
Nishimori I, Bratanova T, Toshkov I, Caffrey T, Mogaki M, Shibata Y, et al. Induction of experimental autoimmune sialoadenitis by immunization of PL/J mice with carbonic anhydrase II. J Immunol. 1995;154:4865–73.
Ueno Y, Ishii M, Takahashi S, Igarashi T, Toyota T, LaRusso NF. Different susceptibility of mice to immune-mediated cholangitis induced by immunization with carbonic anhydrase II. Lab Invest. 1998;78:629–37.
Kountouras J, Zavos C, Gavalas E, Tzilves D. Challenge in the pathogenesis of autoimmune pancreatitis: potential role of Helicobacter pylori infection via molecular mimicry. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:368–9.
Kountouras J, Zavos C, Chatzopoulos D. A concept on the role of Helicobacter pylori infection in autoimmune pancreatitis. J Cell Mol Med. 2005;9:196–207.
Guarneri F, Guarneri C, Benvenga S. Helicobacter pylori and autoimmune pancreatitis: role of carbonic anhydrase via molecular mimicry? J Cell Mol Med. 2005;9:741–4.
Kawa S, Ota M, Yoshizawa K, Horiuchi A, Hamano H, Ochi Y, et al. HLA DRB10405-DQB10401 haplotype is associated with autoimmune pancreatitis in the Japanese population. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1264–9.
McGeachy MJ, Cua DJ. The link between IL-23 and Th17 cell-mediated immune pathologies. Semin Immunol. 2007;19:372–6.
Oukka M. Interplay between pathogenic Th17 and regulatory T cells. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66(Suppl 3):iii87–90.
Yamamoto M, Harada S, Ohara M, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Yamamoto H, et al. Clinical and pathological differences between Mikulicz’s disease and Sjogren’s syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005;44:227–34.
Uchida K, Okazaki K, Nishi T, Uose S, Nakase H, Ohana M, et al. Experimental immune-mediated pancreatitis in neonatally thymectomized mice immunized with carbonic anhydrase II and lactoferrin. Lab Invest. 2002;82:411–24.
Ajjan RA, McIntosh RS, Waterman EA, Watson PF, Franklin CD, Yeoman CM, et al. Analysis of the T-cell receptor Valpha repertoire and cytokine gene expression in Sjogren’s syndrome. Br J Rheumatol. 1998;37:179–85.
Dienes HP, Lohse AW, Gerken G, Schirmacher P, Gallati H, Löhr HF, et al. Bile duct epithelia as target cells in primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Virchows Arch. 1997;431:119–24.
Valencia X, Lipsky PE. CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in autoimmune diseases. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007;3:619–26.
Gottenberg JE, Lavie F, Abbed K, Gasnault J, Le Nevot E, Delfraissy JF, et al. CD4 CD25high regulatory T cells are not impaired in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. J Autoimmun. 2005;24:235–42.
Sakaguchi S, Fukuma K, Kuribayashi K, Masuda T. Organ-specific autoimmune diseases induced in mice by elimination of T cell subset. I. Evidence for the active participation of T cells in natural self-tolerance; deficit of a T cell subset as a possible cause of autoimmune disease. J Exp Med. 1985;161:72–87.
Demols A, Le Moine O, Desalle F, Quertinmont E, Van Laethem JL, Deviere J. CD4(+)T cells play an important role in acute experimental pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2000;118:582–90.
Vallance BA, Hewlett BR, Snider DP, Collins SM. T cell-mediated exocrine pancreatic damage in major histocompatibility complex class II-deficient mice. Gastroenterology. 1998;115:978–87.
Sakaguchi Y, Inaba M, Tsuda M, Quan GK, Omae M, Ando Y, et al. The Wistar Bonn Kobori rat, a unique animal model for autoimmune pancreatitis with extrapancreatic exocrinopathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008;152:1–12.
Marth T, Strober W, Kelsall BL. High dose oral tolerance in ovalbumin TCR-transgenic mice: systemic neutralization of IL-12 augments TGF-beta secretion and T cell apoptosis. J Immunol. 1996;157:2348–57.
Hahm KB, Im YH, Lee C, Parks WT, Bang YJ, Green JE, et al. Loss of TGF-beta signaling contributes to autoimmune pancreatitis. J Clin Invest. 2000;105:1057–65.
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Culture and Science of Japan (20590810), and a Grant-in-Aid for the “Research for Intractable Disease” Program from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okazaki, K., Uchida, K., Koyabu, M. et al. Recent advances in the concept and diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related disease. J Gastroenterol 46, 277–288 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-011-0386-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-011-0386-x