Abstract
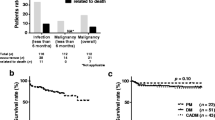
The aim of the study was to estimate the prevalence, characteristics, and prognostic factors of interstitial lung disease (ILD) in patients with polymyositis (PM) and dermatomyositis (DM). The medical records of 151 PM/DM patients treated at Chang Gung Memorial Hospital between January, 2000 and June, 2007 were retrospectively reviewed. Thirty of 151 (19.9%) PM/DM patients had developed ILD. Older age at PM/DM onset, anti-Jo-1 antibody, and arthritis/arthralgia were associated with the presence of ILD (p = 0.004, p = 0.008, and p = 0.026, respectively). Anti-Jo-1 was initially excluded from the multivariate analysis because only 80 patients underwent the test. An older age at onset above 45 years (odds ratio 3.28, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.15–9.34, p = 0.026) and arthritis/arthralgia at onset (odds ratio (OR) 2.57, 95% CI 1.09–6.08, p = 0.032) were the two independent risk factors for developing ILD. If anti-Jo-1 was included in the multivariate analysis (n = 80), then an older age at onset above 45 years (OR 7.30, 95% CI 1.70–31.40, p = 0.008) and anti-Jo-1 positive (OR 7.89, 95% CI 1.18–52.87, p = 0.033) were associated with ILD, while arthritis/arthralgia was no longer significant (OR 2.64, 95% CI 0.70–10.01, p = 0.153). Of the 30 ILD patients, 16 (53.3%) died. The survival time was significantly shorter in ILD patients than in patients without ILD (p < 0.001). Poor survival in ILD patients was associated with male gender (p = 0.039), a Hamman–Rich-like presentation (p = 0.039), and a clinical diagnosis of acute interstitial pneumonia (p = 0.007).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hepper NG, Ferguson RH, Howard FM Jr (1964) Three types of pulmonary involvement in polymyositis. Med Clin North Am 48:1031–1042
Frazier AR, Miller RD (1974) Interstitial pneumonitis in association with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Chest 65:403–407
Fathi M, Lundberg IE (2005) Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 17:701–706
Bohan A, Peter JB (1975) Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med 292:344–347
Euwer RL, Sontheimer RD (1993) Amyopathic dermatomyositis: a review. J Invest Dermatol 100:124S–127S
Chen YJ, Wu CY, Shen JL (2001) Predicting factors of malignancy in dermatomyositis and polymyositis: a case-control study. Br J Dermatol 144:825–831
Ansell BM (1991) Juvenile dermatomyositis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 17:931–942
Hirakata M, Nagai S (2000) Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 12:501–508
Tazelaar HD, Viggiano RW, Pickersgill J et al (1990) Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis: clinical features and prognosis as correlated with histologic findings. Am Rev Respir Dis 141:727–733
Marie I, Hachulla E, Chérin P et al (2002) Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheum 47:614–622
American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias (2002) Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:277–304
Yu KH, Yang CH, Wu YK et al (2006) Diffuse alveolar damage as the initial presentation of dermatomyositis and successfully treated with intravenous immunoglobulin and steroids: a case report. J Musculoskel Pain 14:45–50
MIills ES, Mathews WH (1956) Interstitial pneumonitis in dermatomyositis. J Am Med Assoc 160:1467–1470
Fujisawa T, Suda T, Nakamura Y et al (2005) Differences in clinical features and prognosis of interstitial lung diseases between polymyositis and dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol 32:58–64
Ye S, Chen XX, Lu XY et al (2007) Adult clinically amyopathic dermatomypsitis with rapid progressive interstitial lung disease: a retrospective cohort study. Clin Rheumatol 26:1647–1654
Schnabel A, Reuter M, Biederer J et al (2003) Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis: clinical course and response to treatment. Semin Arthitis Rheum 32:273–284
Fathi M, Dastmalchi M, Rasmussen E et al (2004) Interstitial lung disease, a common manifestation of newly diagnosed polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Ann Rheum Dis 63:297–301
Grau JM, Miró O, Pedrol E et al (1996) Interstitial lung disease related to dermatomyositis: comparable study with patients without lung involvement. J Rheumatol 23:1921–1926
Kang EH, Lee EB, Shin KC et al (2005) Interstitial lung disease in patients with polymyositis, dermatomyositis and amyopathic dermatomyositis. Rheumatology 44:1282–1286
Dankó K, Ponyi A, Constantin T, Borgulya G, Szegedi G (2004) Long-term survival of patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies according to clinical features: a longitudinal study of 162 cases. Medicine 83:35–42
Selva-O'Callaghan A, Labrador-Horrillo M, Muñoz-Gall X et al (2005) Polymyositis/dermatomyositis-associated lung disease: analysis of a series of 81 patients. Lupus 14:534–542
Chen YJ, Wu CY, Shen JL (2007) Predicting factors of interstitial lung disease in dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Acta Derm Venereol 87:33–38
Stone KB, Oddis CV, Fertig N et al (2007) Anti-Jo-1 antibody levels correlated with disease activity in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. Arthritis Rheum 56:3125–3131
Mielnik P, Wiesik-Szewczyk E, Olesinska M et al (2006) Clinical features and prognosis of patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and anti-Jo-1 antibodies. Autoimmunity 39:243–247
Suda T, Fujisawa T, Enomoto N et al (2006) Interstitial lung disease associated with amyopathic dermatomyositis. Eur Respir J 28:1005–1012
Douglas WW, Tazelaar HD, Hartman TE et al (2001) Polymyositis-dermatomyositis- associated interstitial lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:1182–1185
Tansey D, Wells AU, Colby TV et al (2004) Variations in histological patterns of interstitial pneumonia between connective tissue disorders and their relationship to prognosis. Histopathology 44:585–596
Cottin V, Thivolet-Béjui F, Reynaud-Gaubert M et al (2003) Interstitial lung disease in amyopathic dermatomyositis, dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Eur Respir J 22:245–250
Won Huh J, Soon Kim D, Keun Lee C et al (2007) Two distinct clinical types of interstitial lung disease associated with polymyositis-dermatomyositis. Respir Med 101:1761–1769
Ito M, Kaise S, Suzuki S et al (1999) Clinico-laboratory characteristics of patients with dermatomyositis accompanied by rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease. Clin Rheumatol 18:462–467
Oddis CV (2000) Current approach to the treatment of polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 12:492–497
Nawata Y, Kurasawa K, Takabayashi K et al (1999) Corticosteroid resistant interstitial pneumonitis in polymyositis/dermatomyositis: prediction and treatment with cyclosporine. J Rheumatol 26:1527–1533
Yoshida T, Koga H, Saitoh F et al (1999) Pulse intravenous cyclophosphamide treatment for steroid-resistant interstitial pneumonitis associated with polymyositis. Intern Med 38:733–738
Dalakas MC, Illa I, Dambrosia JM et al (1993) A controlled trial of high-dose intravenous immune globulin infusions as treatment for dermatomyositis. N Engl J Med 329:1993–2000
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, IJ., Jan Wu, YJ., Lin, CW. et al. Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Clin Rheumatol 28, 639–646 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1110-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1110-6