Abstract
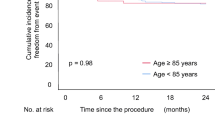
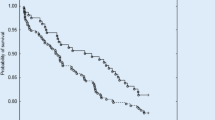
Pacemakers are frequently implanted, yet accurate prospective data on implant complications are limited. Elderly patients may be at increased risk of implant complications and are increasingly being referred for pacemaker implantation. The purpose of the present analysis was to define the incidence and possible predictors of serious complications of dual chamber permanent pacemaker implantation in the elderly. Therefore, we sought to prospectively identify the incidence and predictors of pacemaker implant complications in a large multicenter trial involving patients receiving a dual chamber pacemaker. The Pacemaker Selection in the Elderly (PASE) study was a prospective trial designed to evaluate quality of life in dual chamber pacemaker recipients age 65 years or older randomized to DDDR versus VVIR programming. In addition to being age 65 years or older, patients enrolled in this study were in normal sinus rhythm, and had standard indications for permanent pacemaker implantation. All patients received dual chamber pacemakers and were randomized to DDDR versus VVIR pacing. Pacemaker implant complications were collected on standardized forms which were completed at pacemaker implantation and during follow-up appointments. In this study of 407 patients, there were 26 complications occurring in 25 patients (6.1%). The most frequent complication was lead dislodgment which occurred in 9 patients. This was followed by pneumothorax (8 patients) and cardiac perforations (4 patients). In 18 patients (4.4%) repeat surgical procedures (including chest tubes) were required. Complications were noted prior to discharge in only 18 patients. There were no significant predictors of overall complications. Pneumothorax was more frequent in patients ≤75 years old, and was observed only in patients with subclavian venous access. In conclusion, complications from pacemaker implantation in the elderly are seen in 6.1% of patients and 4.4% of patients require a repeat surgical procedure. Other than advanced age and lower weight predicting for pneumothorax, there are no significant clinical predictors of complications
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernstein AD, Parsonnet V. Survey of cardiac pacing and defibrillation in the United States in 1993. Am J Cardiol 1996;78:187-196.
Chauhan A, Grace AA, Newell SA, et al. Early complications after dual chamber versus single chamber pacemaker implantation. PACE 1994;17:2012-2015.
Aggarwal RK, Connelly DT, Ray SG, Ball J, Charles RG. Early complications of permanent pacemaker implantation: No difference between dual and single chamber systems. Br Heart J 1995;73:571-575.
Lamas GA, Ellenbogen KA, Griffin JJ, et al. Quality of life and clinical events in DDDR versus VVIR paced patients: Design and preliminary results of a randomized trial. Circulation 1995;92(Suppl 1):I-533(Abstract).
Goldman L, Hashimoto B, Cook F, Loscalzo A. Comparative reproducibility and validity of systems for assessing cardiovascular functional class: Advantages of a new specific activity scale. Circulation 1981;64:1227-1234.
Mor V, Laliberte L, Morris JN, Wieman M. The Karnofsky performance status scale: An examination of its reliability and validity in a research setting. Cancer 1984;53:2002-2007.
Cox DR. Regression models and life-tables. J R Stat Soc 1972;34:187-188.
Kaplan EL, Meier P. Nonparametric estimations from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 1958;53:457-458.
Klovekorn WP, Struck E, Sasa T. Complications after pacemaker-implantation and their treatment (German). Herz 1978;63:357-361.
Bucking J, Voss H, Stein J, Hahner U. Early and late complications of endocardial pacemaker wires (German). Zeit fur Kardiol 1980;69:427-431.
Hill PE. Complications of permanent transvenous cardiac pacing: A 14 year review of all transvenous pacemakers inserted at one community hospital. PACE 1980;10:564-570.
Parsonnet V, Bernstein A, Lindsay B. Pacemaker-implantation complication rates: An analysis of some contributing factors. J Am Coll Cardiol 1989;13:917-921.
Mueller X, Sadeghi H, Kappenberger L. Complications after single versus dual chamber pacemaker implantation. PACE 1990;13:711-714.
Mounsey JP, Griffith MJ, Tynan M, et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis in permanent pacemaker implantation: A prospective randomized trial. Br Heart J 1994;72:339-343.
Lamas GA. The MOST study. Heart 1997;78:218-220
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Link, M.S., Estes, N.M., Griffin, J.J. et al. Complications of Dual Chamber Pacemaker Implantation in the Elderly . J Interv Card Electrophysiol 2, 175–179 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009707700412
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009707700412