Abstract
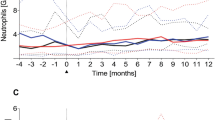
Rituximab is an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody that has efficacy in B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL). Adjuvant immunotherapy with rituximab may reduce relapse rates for high-risk B-cell NHL following high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell transplantation (SCT). However, the potential adverse effects of rituximab on immune reconstitution following SCT are not fully characterized. We performed a retrospective analysis of immunoglobulin (Ig) levels and peripheral blood neutrophil counts in 11 patients who received adjuvant rituximab following autologous SCT for B-cell NHL. Results were compared to a contemporaneous group of 24 patients who received an identical conditioning regimen and autologous SCT for lymphoma, but no adjuvant rituximab. Adjuvant rituximab was associated with a significantly increased incidence of hypogammaglobulinaemia between 12 and 24 months post-SCT, but not neutropenia. Despite suppression of Igs, there were no late or atypical infective complications attributable to rituximab.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others

References
Philip T, Guglielmi C, Hagenbeek A, Somers R, Van Der Lelie H, Bron D et al. Autologous bone marrow transplantation as compared with salvage chemotherapy in relapses of chemotherapy-sensitive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: 1540–1545.
Malek SN, Flinn IW . Incorporating monoclonal antibodies in blood and marrow transplantation. Semin Oncol 2003; 30: 520–530.
Brugger W, Hirsch J, Grunebach F, Repp R, Brossart P, Vogel W et al. Rituximab consolidation after high-dose chemotherapy and autologous blood stem cell transplantation in follicular and mantle cell lymphoma: a prospective, multicenter phase II study. Ann Oncol 2004; 15: 1691–1698.
Shimoni A, Hardan I, Avigdor A, Yeshurun M, Raanani P, Ben-Bassat I et al. Rituximab reduces relapse risk after allogeneic and autologous stem cell transplantation in patients with high-risk aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2003; 122: 457–464.
Horwitz SM, Negrin RS, Blume KG, Breslin S, Stuart MJ, Stockerl-Goldstein KE et al. Rituximab as adjuvant to high-dose therapy and autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation for aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2004; 103: 777–783.
Goldberg SL, Pecora AL, Alter RS, Kroll MS, Rowley SD, Waintraub SE et al. Unusual viral infections (progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and cytomegalovirus disease) after high dose chemotherapy with autologous blood stem cell rescue and peritransplant rituximab. Blood 2002; 99: 1486–1488.
Reff ME, Carner K, Chambers KS, Chinn PC, Leonard JE, Rabb R et al. Depletion on B cells in vivo by a chimeric mouse human antibody to CD20. Blood 1994; 83: 435–445.
Maloney D, Smith B, Appelbaum F . The anti-tumor effect of monoclonal anti CD-20 includes direct anti-proliferative activity and induction of apoptosis in CD20 positive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma cell lines. Blood 1996; 88: 637a.
Coiffier B, Haioun C, Ketterer N, Engert A, Tilly H, Ma D et al. Rituxumab (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody) for the treatment of patients with relapsing or refractory aggressive lymphoma: a multicenter phase II study. Blood 1998; 92: 1927–1932.
Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, Herbrecht R, Tilly H, Bouabdallah R et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 235–242.
McLaughlin P, Grillo-Lopez AJ, Link BR, Levy R, Czuczman MS, Williams ME et al. Rituximab chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy for relapsed indolent lymphoma: half of patients respond to a four-dose treatment program. J Clin Oncol 1998; 16: 2825–2833.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shortt, J., Spencer, A. Adjuvant rituximab causes prolonged hypogammaglobulinaemia following autologous stem cell transplant for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant 38, 433–436 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705463
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705463
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Persistent hypogammaglobulinemia due to immunoglobulin class switch impairment by peri-transplant rituximab therapy
International Journal of Hematology (2020)
-
B- and T-lymphocyte number and function in HIV+/HIV− lymphoma patients treated with high-dose chemotherapy and autologous bone marrow transplantation
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Prolonged clinical remissions in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma treated with autologous stem cell transplantation incorporating rituximab
Annals of Hematology (2015)
-
Reactivation of hepatitis B virus following rituximab-plus-steroid combination chemotherapy
Journal of Gastroenterology (2011)
-
Severe hypogammaglobulinemia persisting for 6 years after treatment with rituximab combined chemotherapy due to arrest of B lymphocyte differentiation together with alteration of T lymphocyte homeostasis
International Journal of Hematology (2010)