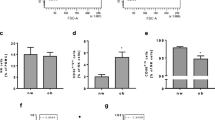
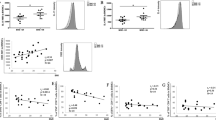
Background: Obesity affects the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses. This study characterizes differences in peripheral blood lymphocyte phenotype in obese humans. Methods: Frequencies of lymphocyte subsets among peripheral blood mononuclear cells were compared between 10 obese (BMI ≥35) and 10 lean subjects, as determined by antibodies directed against cluster differentiation (CD) markers. Results: Obese patients demonstrated an increased frequency of CD3+CD4+ T-cells (mean difference 12%, P=0.004), a decreased frequency of CD3+CD8+ T-cells (mean difference 9.4%, P=0.016) and an increased frequency of CD3+CD8+CD95+ T-cells (mean difference 13.3%, P=0.032). No other differences among T-cell or monocyte subsets were noted. Conclusions: Obesity is associated with alterations in frequencies of peripheral CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells and aberrations in the expression of CD95 among CD8+ T-cells. These data suggest both CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell compartments, as well as the regulation of CD95 expression on CD8+ T-cells, as targets for further study into obesity's effects on the immune system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O'Rourke, R.W., Kay, T., Scholz, M.H. et al. Alterations in T-Cell Subset Frequency in Peripheral Blood in Obesity. OBES SURG 15, 1463–1468 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1381/096089205774859308
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1381/096089205774859308